 출처 : https://velog.io/@yejinh/비동기-파헤치기
출처 : https://velog.io/@yejinh/비동기-파헤치기
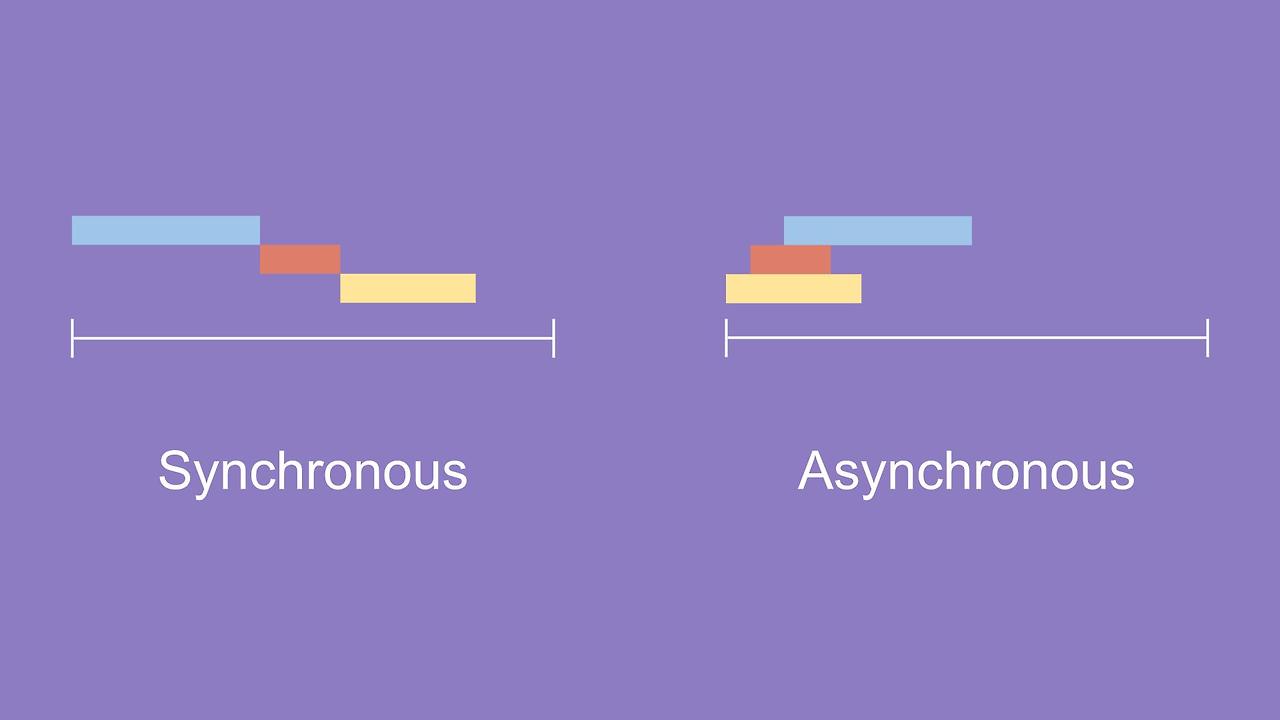
Asynchronous(비동기)
요청을 하고 순차적으로 결과를 기다리지 않고 다음 할 일을 진행
추후에 작업 결과를 확인하고 싶은 경우 Future 등을 이용하여 확인 가능하다.
@Async
스프링에서 비동기 처리를 지원하는 애노테이션
사용 방법
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class MySpringApplication {
...
}
public class AsyncService {
@Async
public void method(){
...
}
}
�Thread Pool
위와 같이 사용하면 @Async가 붙은 메서드는 별도의 스레드에서 동작한다.
다만, 기본적으로 비동기 처리를 할 때 ( org.springframework.core.task.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor ) executor를 통해서 이루어지는데 고려해야 할 사항이 존재한다.
- 요청이 이루어질 때마다 새로운 thread를 생성
- thread pool을 이용하여 재사용을 하는 구조가 아님
- 요청이 많은 API의 경우에는 자원 고갈 문제가 발생 할 수 있음
thread pool을 지정해서 사용하고 싶은 경우에는 @Async 애너테이션 프로퍼티로 threadPoolTaskExecutor를 작성하면 된다.
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class MySpringApplication {
@Bean(name = "threadPoolTaskExecutor")
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(2);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(10);
executor.setQueueCapacity(50);
return executor;
}
}
public class AsyncService {
@Async("threadPoolTaskExecutor")
public void method(){
...
}
}
Proxy 방식
@Async 애노테이션은 Spring의 AOP 방식인 proxy를 통해 동작이 이루어진다.
Proxy 방식인 경우 주의해야 할 사항을 주의해야 한다.
https://kkang-joo.tistory.com/58
- self invocation
- private method
Exception Handling
@Async에서 발생한 예외는 호출자에게 전파되지 않는다.
@Async에서 발생한 예외를 Custom 하게 처리하기 위해서는 별도의 AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler가 필요
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class MySpringApplication extends AsyncConfigurerSupport {
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return new TestAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler();
}
}
public class TestAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler implements AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler {
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable throwable, Method method, Object... obj) {
...
}
}